Introduction:
Cancer is not a single disease but a group of diseases that develop when the body’s normal cell control system fails. Instead of growing, dividing, and dying in an orderly way, abnormal cells continue to multiply and form masses known as tumors. These cancer cells can damage nearby tissues and may travel to distant organs through blood or lymph channels.
Many people fear with different stages of cancer because it is often detected late. However, when cancer is identified early and managed properly, survival chances improve significantly. Learning about cancer stages, early symptoms, and prevention strategies empowers people to seek medical care at the right time.
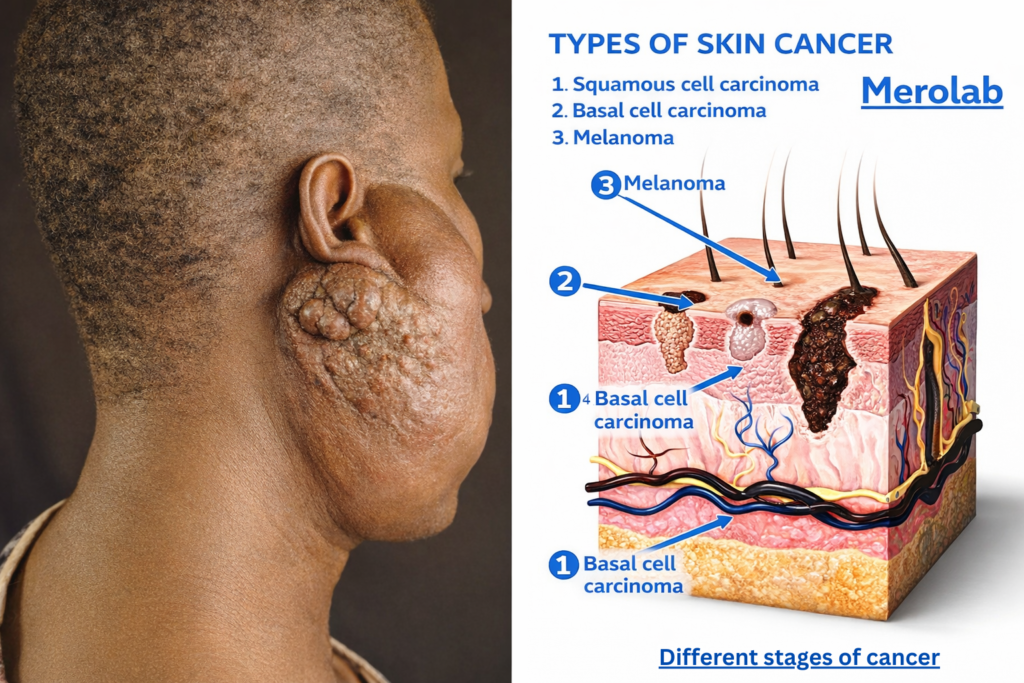
different-stages-of-cancer-understanding-type-symptoms and way to prevent Cancer. cancer is not a single disease but a group of diseases that develop when the body’s normal cell control system fails. Instead of growing, dividing, and dying in an orderly way, abnormal cells continue to multiply and form masses known as tumors. These cancer cells can damage nearby tissues and may travel to distant organs through blood or lymph channels.
How Cancer Stages Are Defined
Different Stages of Cancer in 21st century, Cancer staging explains how far the disease has progressed inside the body. Doctors use staging to decide treatment options and estimate recovery chances.
Stage 0: Very Early Cancer
At this stage, abnormal cells are present only in the surface layer of tissue. These cells have not invaded nearby structures or spread elsewhere. Many screening programs aim to detect cancer at this stage.
- Treatment is usually simple
- Cure rate is extremely high
Stage I: Early-Stage Cancer
Stage I cancer means the tumor is small and limited to one area. There is no spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. Symptoms may be mild or absent.
Surgery alone may be enough.
Recovery rate is excellent.
Stage II: Local Spread
Here, the cancer has grown larger and may have started affecting nearby tissues. Some lymph nodes might be involved, but the disease is still localized.
Treatment may include surgery plus medication or radiation.
Early action is still very effective.
Stage III: Regional Spread
Stage III cancer indicates that cancer cells have reached nearby lymph nodes or surrounding tissues. Symptoms become more noticeable at this stage.
Requires combined treatment approaches.
Close medical monitoring is essential.
Stage IV: Advanced or Metastatic Cancer
This is the most advanced stage, where cancer cells have spread to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, brain, or bones. Although cure may not be possible, modern treatments can slow progression and reduce suffering.
Focus on life extension and comfort.
Symptom control is a priority.
Warning Signs That Should Never Be Ignored
Different Stages of Cancer can show itself in many ways. While symptoms differ between individuals, some common warning signs include:
- Unplanned weight loss without dieting
- Persistent tiredness even after rest
- Pain that remains for weeks or months
- A growing lump or swelling
- Changes in skin appearance or texture
- Bleeding that is unusual or unexplained
- Long-lasting cough or breathing difficulty
- Changes in bowel or urinary habits
These signs do not always mean cancer, but they should always be medically evaluated.
Overview of Common Cancer Types
Bladder Cancer
Often begins with blood in the urine. Some people also experience burning sensation or frequent urination. Early diagnosis allows effective treatment.
Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer May appear as a painless lump, changes in breast shape, skin thickening, or nipple discharge. Regular self-checks and screening help detect it early.
Colorectal Cancer
Symptoms include altered bowel habits, blood in stool, and abdominal discomfort. This cancer develops slowly, making screening very important.
Kidney Cancer
Blood in urine, lower back pain, and general weakness may occur. In many cases, early stages show no symptoms.
Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Characterized by chronic cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and sometimes coughing blood. Smoking and air pollution are major risk factors.
Lymphoma
This cancer affects the immune system. Painless swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss are common signs.
Pancreatic Cancer
Often presents late with symptoms like jaundice, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. Early detection remains challenging.
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer symptoms include difficulty urinating and weak urine flow. Many cases grow slowly and respond well to early treatment.
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer appears as new or changing moles, patches, or wounds that do not heal. Excessive sun exposure increases risk.
Uterine Cancer
Commonly causes abnormal vaginal bleeding and pelvic discomfort. Early gynecological evaluation is crucial.
Special Cancer Conditions
Metastatic Cancer
This occurs when cancer spreads from its original site to other organs. Even after spreading, treatment is based on the original cancer type.
Recurrent Cancer
Cancer that returns after treatment is known as recurrent cancer. It may reappear in the same location or a different part of the body.
Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer focuses on symptom relief, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life rather than cure.
Emotional and Psychological Impact of Cancer
Different Stages of Cancer affects mental health as much as physical health. Fear, anxiety, and depression are common among patients and caregivers.
Helpful support includes:
- Open communication with family
- Counseling and support groups
- Proper nutrition and rest
- Gentle physical activity
- Stress management practices
Managing Cancer Treatment Effectively
Different Stages of Cancer care is most successful when multiple healthcare professionals work together. Diagnosis, laboratory testing, imaging, treatment, and follow-up must be coordinated.
Laboratory investigations play a key role in:
- Confirming diagnosis
- Monitoring treatment response
Detecting recurrence early
Cancer in Young People and Children
Cancer in adolescents can disrupt education and emotional development. Childhood cancers, although rare, often respond well to treatment when detected early.
Early medical attention and supportive care make a major difference.
How Cancer Risk Can Be Reduced
While cancer cannot always be prevented, risk can be lowered by:
- Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol
- Eating fresh fruits and vegetables
- Staying physically active
- Maintaining healthy body weight
- Protecting skin from excessive sun exposure
- Receiving recommended vaccinations
- Participating in regular health screenings
Conclusion:
Cancer is a challenging disease, but knowledge is one of the strongest tools in fighting it. Understanding Different Stages of cancer, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting healthy habits can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes. Awareness, education, and timely medical care save lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does “cancer stage” actually mean?
A cancer stage describes how much cancer is in the body and how far it has spread. Doctors use staging to decide the best treatment plan and to understand the likely outcome.
What are the stages of cancer?
Cancer is divided into five stages (0 to IV), which show how big the tumor is and whether it has spread.
What is the difference between Stage I and Stage II?
Stage I: Small tumor, limited to one area, no spread to lymph nodes.
Stage II: Larger tumor, may have spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
What happens in Stage III cancer?
Stage III cancer has spread more to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
What is Stage IV cancer?
Stage IV, or advanced cancer, has spread to distant organs. Treatment focuses on controlling the disease and improving quality of life.
Can cancer be cured at any stage?
Early-stage cancers (0–II) have high treatment success. Even advanced cancers (III–IV) can be managed with modern therapies.
Can early detection prevent advanced cancer?
Yes. Screening and regular checkups can detect cancer early, when treatment is more effective.
